Written by:

Medically Reviewed by:
Last Updated:
April 10th, 2025
Drug Addiction | Types, Symptoms and Effects
- Select
- Drug addiction
- Drug detox
- Drug rehab
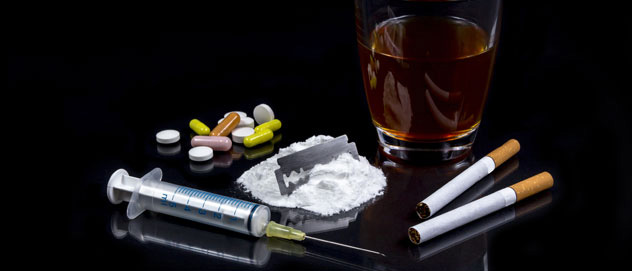
Drug addiction continues to plague many individuals and communities across the world. It is an affliction that cuts across all economic, social, racial and ethnic backgrounds with devastating results. Not only does drug addiction cause untold physical and psychological harm, but it can also lead to financial difficulties, legal issues and relationship problems – so much so that you barely recognise the life before you.
If this is the case for you, Recovery Lighthouse can help you get your life back on track. Our team is committed to your success and will support you as you make the transition to a healthier life.
Why are drugs addictive?
The neurotransmitter dopamine is associated with memory, motivation and our experience of satisfaction or ‘rewards’ from any activity. When drugs enter your system, they artificially skew the dopamine balance in the brain and create an abnormal positive reward response. Neuroadaptations occur in this reward pathway, leading to intense cravings for more drugs in order to get the same ‘reward’ again.
As time goes on, you may have difficulty refraining from taking drugs as your brains become rewired for increased drug-seeking behaviour. Eventually the brain will stop producing its own dopamine, instead relying on substances. This means that if you try to quit, you will likely experience uncomfortable withdrawal symptoms as your brain tries to adapt.
How does drug addiction develop?
In most cases, drug addiction develops over time and can usually be outlined by four stages:
- Experimentation: in the early stages of experimentation, you may use drugs recreationally, as a result of curiosity. This could be because you want to have fun, or because you are trying to cope with a stressful situation.
- Regular use: drug use moves from occasional to regular during the second stage. The potential for abuse is high, however, it is important to note that regular use does not equate to an addiction yet.
- High-risk use: as substance misuse progresses, you may engage in more risky behaviour and continue to use drugs despite any social or legal consequences. You may notice yourself becoming preoccupied with using and could experience cravings.
- Addiction and dependency: eventually your brain and body will become dependent on drugs, needing them just to feel normal. You will engage in compulsive drug use and find it very difficult to stop without professional intervention.
The timeline for a drug addiction developing is different for everyone – while for some this can occur in a matter of weeks, for others it may take much longer. This largely depends on the substance you are abusing and its addictive qualities, how the drug is consumed, as well as your own individual physiology and circumstances.
Who is at risk of drug addiction?
Drug addiction can impact anyone, but there are some potential risk factors that could increase the chances of a problem developing. These genetic, environmental and physical factors often work together to propel you towards drug abuse and addiction.
Some of these risk factors include:
- Genetics: having a family history of drug addiction means you may have a genetic predisposition.
- Using drugs at an early age: as your brain is still developing, the effects of drugs have more of an impact, meaning an addiction is more likely to form as you get older.
- Mental health disorders: those who suffer from mental health issues like depression, anxiety, PTSD and schizophrenia are more likely to develop a drug addiction as they may use substances to self-medicate.
- Abuse or trauma: if you have experienced abuse or trauma in the past, you are more likely to abuse substances as a way to escape reality and are therefore more likely to develop an addiction.
- Living in poverty: those living in unstable environments with difficult social circumstances may also be more prone to developing an addiction.
Identifying the most vulnerable and taking steps to prevent drug addiction is crucial. If you fall into one of these categories and would like help, speak to your doctor or local healthcare provider, or alternatively give the Recovery Lighthouse team a call.
Taking drugs: the dangers
Taking drugs is a high-risk activity with far-reaching consequences for an individual’s physical and psychological well-being. While a person may initially seek the pleasurable effects of substances, their continued use can lead to dependency, mental health complications, dangerous physical side effects and even neurological damage.
While different drugs carry different health dangers, some of the most common risks include:
- Nausea, vomiting or abdominal pain
- A weakened immune system
- Damage to internal organs
- Increased risk of heart attack, stroke, seizures and other life-threatening issues
- Decreased cognitive function, difficulty concentrating and issues with memory
- Increased risk of mental health issues, including depression and anxiety
- Danger of overdose and death
Perhaps you are already suffering from some of these consequences, or perhaps you are worried that this could be in your future. Wherever you are in your drug addiction, Recovery Lighthouse can turn your life around. Don’t wait until it’s too late to get the help you need.
How to spot a drug addiction
Spotting a drug addiction in a loved one can be challenging, as the common signs may not always be obvious. However, there are some key warning signs to pay attention to that may indicate a problem with drugs.
Some of the signs of drug addiction include:
- Decline in performance at work or school
- Lack of hygiene
- Always turning up late or cancelling plans
- Frequently being uncontactable
- Secretive behaviour
- Mood swings and irritability
- Decreased energy levels and changes to sleep patterns
- Changes to appetite that may lead to weight loss
- Changes in social circle
- Changes in appearance – they may have dark circles under their eyes or appear unhealthy
- Inability to keep up with day-to-day responsibilities
- Asking to borrow money or even stealing money to fuel their habit
If you have noticed any of these signs in a family member, the next step is to reach out and offer your support. This is notoriously tricky, and may evoke feelings of anxiety and worry just thinking about it. However, having this conversation could be the wake-up-call your loved one needs.
What drugs are the most addictive?
Heroin, crack cocaine, meth, benzodiazepines, and prescription opioids are among the most addictive substances and can quickly pull you into a spiral of abuse and addiction. If you think you could be addicted to any of these substances, it is important that you seek professional help as soon as possible.
![]()
Amphetamine addiction
Learn more about the signs, symptoms and effects of a amphetamine addiction.

Cannabis addiction
Learn more about the signs, symptoms and effects of a cannabis addiction.

Cocaine addiction
Learn more about the signs, symptoms and effects of a cocaine addiction.

Crack cocaine addiction
Learn more about the signs, symptoms and effects of a crack cocaine addiction.

Ecstasy addiction
Learn more about the signs, symptoms and effects of a ecstasy addiction.
Heroin addiction
Learn more about the signs, symptoms and effects of a heroin addiction.
Ketamine addiction
Learn more about the signs, symptoms and effects of a ketamine addiction.

Meth addiction
Learn more about the signs, symptoms and effects of a meth addiction.
![]()
Monkey dust addiction
Learn more about the signs, symptoms and effects of a amphetamine addiction.
Talking to a loved one about drug addiction
If you suspect a family member is struggling with an addiction to drugs, it is important to approach the situation with consideration and empathy. When opening a conversation, it may be beneficial to demonstrate an understanding of why the person has turned to drugs, as this will show that your primary concern is their well-being and not criticism.
Choose the right time to approach your loved one – they should be sober if possible, and in a private space. Take time to understand the depth of the issue, offer your support and avoid accusations. Talk with them instead of lecturing them, ask how they are feeling and listen carefully to their response.
It is never easy to have these conversations, but maybe this could be the starting point for your loved one’s recovery. If they are not quite ready to get the help they need, make sure you set boundaries and let them know that you’ll be there for them when they do decide to start treatment.
Is there treatment available for drug addiction?
There are several treatment options available to help people overcome drug addiction: inpatient rehab programs are one of the most popular and successful. Recovery Lighthouse offers a safe and comfortable space where you can heal from past traumas and learn healthier behaviour patterns. Our programme relies on scientifically-proven therapies, as well as holistic activities such as yoga, art therapy and meditation, to treat both the physical and psychological aspects of your addiction.
Next steps
Drug addiction is a serious condition that has the potential to cause significant harm. While taking that first step and admitting you need help is tough, it also sets you on the path to a healthier and more fulfilling life. Recovery Lighthouse can help you to build a brighter future for yourself, and provide you with the skills and knowledge you need to maintain your sobriety.
It is never too early for drug addiction treatment. In fact, the earlier you start, the easier your recovery will be. You do not have to wait until rock bottom to get help. If you would like more information on our programmes or you would like to start your journey to a drug-free life, please get in touch. Our admissions team is available 24/7 and is happy to answer any questions you may have.